Weekly Alert: IT Cybersecurity Support
Our Weekly Threat Intelligence Summary is compiled by expert threat analysts, highlighting the key threat events you should know about and offering mitigation recommendations.
Top Intelligence Events
 Threat Brief (High):
Threat Brief (High):
Fortinet Releases Critical FortiSwitch Patch Alongside Multiple Vulnerability Advisories
On April 8, 2025, Fortinet released multiple PSIRTs, including one critical-rated vulnerability affecting FortiSwitch (CVE-2024-48887, rated 9.3/10). The flaw enables an unauthenticated remote attacker to modify administrator passwords via specially crafted HTTP requests to the “set_password” endpoint in the FortiSwitch GUI.
This vulnerability stems from an unverified password change mechanism, making it a serious concern for any internet-exposed or misconfigured FortiSwitch deployments. Fortinet’s provided workaround is to disable HTTP/HTTPS access from administrative interfaces or to lock access down to trusted hosts.
Multiple firmware branches are affected, spanning FortiSwitch versions 6.4 through 7.6. Fortinet has issued updates to mitigate the issue, and administrators are strongly urged to upgrade as soon as possible.
In addition to the critical vulnerability, a High-severity flaw (CVE-2024-26013 & CVE-2024-50565, rated 7.1/10) was also disclosed affecting FortiAnalyzer, FortiManager, FortiOS, FortiProxy, FortiVoice, and FortiWeb. The issue involves improper certificate validation during FGFM connections, which could allow a man-in-the-middle attacker to impersonate trusted management devices. Organizations relying on Fortinet’s centralized management or FortiCloud should prioritize patching to prevent potential exploitation.
Organizations using Fortinet products should:
- Review your firmware versions and ensure the devices are up to date in accordance with Fortinet’s recommended solutions listed in their PSIRT advisories.
- Limit GUI Exposure by disabling HTTP/HTTPS access to administrative interfaces whenever possible.
- Restrict admin access via Fortinet’s trusted host configuration to reduce exposure surface.
Threat Brief (High):
Microsoft’s April 2025 Patch Tuesday Addresses 1 Actively Exploited Zero-Day, 126 Vulnerabilities
Microsoft has released its April 2025 Patch Tuesday security updates, providing fixes for a total of 126 vulnerabilities, including one actively exploited zero-day vulnerability. Of the patches released, 11 are rated “Critical”, all are remote code execution vulnerabilities.
The actively exploited zero-day vulnerability can be found below:
- CVE-2025-29824 – An important elevation of privilege vulnerability affecting Windows Common Log File System and has a CVSS score of 7.8. This could allow a remote attacker to run arbitrary code on a victim machine after tricking a victim into either opening a malicious file from an email or message, or navigating to an adversary-owned website. Updates for Windows 10 32-bit and x64 systems are pending release.
Microsoft shared more details about how the vulnerability was exploited as a zero-day. The attacks were linked to the RansomEXX ransomware gang, which it tracks as Storm-2460, to gain elevated privileges. The targets include organizations in the information technology (IT) and real estate sectors of the United States, the financial sector in Venezuela, a Spanish software company, and the retail sector in Saudi Arabia.
The complete list of all the other vulnerabilities released for Microsoft’s April 2025 Patch Tuesday update can be found here.
Organizations should review the April 2025 security updates, apply patches to affected systems as soon as possible, and regularly scan the environment to identify systems yet to be patched.
- Patching should focus on the actively exploited vulnerability described above and critical vulnerabilities.
- Reviewing individual CVEs from Microsoft will also provide workarounds/mitigations if immediate patching is not possible.
Threat Hunting
- Threat Hunt: Neptune RAT
- Date: 04/10/25
- Log Dependencies: EDR Solutions (SentinelOne and CrowdStrike), eSIEMSummary: Neptune is a Remote Access Trojan (RAT) written in Visual Basic .NET. It incorporates multiple features like stealing credentials from over 270 apps, deploying ransomware, and even monitoring desktops in real-time. It tries to avoid antivirus detection and employs anti-analysis techniques to hide its activities. This malware also makes use of the catbox[.]me API to store malicious scripts and files. Recently, the latest version of the malware was shared on GitHub by its developer.
Top Intelligence Trends
Vulnerabilities
Below are the top five trending vulnerabilities of the week. Trends are determined by criticality, activity, mentions, and exploitability. If your organization uses any of these technologies, you should prioritize patching against these threats.
- CVE-2025-0282 – A stack-based buffer overflow in Ivanti Connect Secure before version 22.7R2.5, Ivanti Policy Secure before version 22.7R1.2, and Ivanti Neurons for ZTA gateways before version 22.7R2.3 allows a remote unauthenticated attacker to achieve remote code execution.
- CVE-2025-29927 – Next.js is a React framework for building full-stack web applications. Prior to 14.2.25 and 15.2.3, it is possible to bypass authorization checks within a Next.js application, if the authorization check occurs in middleware. If patching to a safe version is infeasible, it is recommended that you prevent external user requests which contain the x-middleware-subrequest header from reaching your Next.js application. This vulnerability is fixed in 14.2.25 and 15.2.3.
- CVE-2024-55591 – An Authentication Bypass Using an Alternate Path or Channel vulnerability [CWE-288] affecting FortiOS version 7.0.0 through 7.0.16 and FortiProxy version 7.0.0 through 7.0.19 and 7.2.0 through 7.2.12 allows a remote attacker to gain super-admin privileges via crafted requests to Node.js websocket module.
- CVE-2025-24813 – Path Equivalence: ‘file.Name’ (Internal Dot) leading to Remote Code Execution and/or Information disclosure and/or malicious content added to uploaded files via write enabled Default Servlet in Apache Tomcat. This issue affects Apache Tomcat: from 11.0.0-M1 through 11.0.2, from 10.1.0-M1 through 10.1.34, from 9.0.0.M1 through 9.0.98. If all of the following were true, a malicious user was able to view security sensitive files and/or inject content into those files: – writes enabled for the default servlet (disabled by default) – support for partial PUT (enabled by default) – a target URL for security sensitive uploads that was a sub-directory of a target URL for public uploads – attacker knowledge of the names of security sensitive files being uploaded – the security sensitive files also being uploaded via partial PUT If all of the following were true, a malicious user was able to perform remote code execution: – writes enabled for the default servlet (disabled by default) – support for partial PUT (enabled by default) – application was using Tomcat’s file based session persistence with the default storage location – application included a library that may be leveraged in a deserialization attack Users are recommended to upgrade to version 11.0.3, 10.1.35 or 9.0.99, which fixes the issue.
- CVE-2025-0411 – 7-Zip Mark-of-the-Web Bypass Vulnerability. This vulnerability allows remote attackers to bypass the Mark-of-the-Web protection mechanism on affected installations of 7-Zip. User interaction is required to exploit this vulnerability in that the target must visit a malicious page or open a malicious file. The specific flaw exists within the handling of archived files. When extracting files from a crafted archive that bears the Mark-of-the-Web, 7-Zip does not propagate the Mark-of-the-Web to the extracted files. An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user.
InfoStealer Malware
The Threat Intelligence Team is constantly analyzing data from dark web marketplaces to keep a pulse on InfoStealer malware trends. The team identifies and studies these covert threats to arm our clients and guide our threat hunting operations. Our analysis of these cybercriminal exchanges aids in predicting and countering these InfoStealer threats, safeguarding our clients’ digital assets.

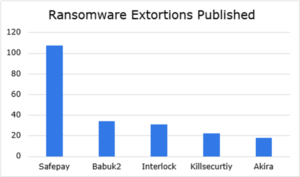
Ransomware Actors
Fizen Technology
Have questions? Contact us if you have technology questions for your business. We are here to help you with your IT needs, so you can focus on your business. Thank you to our partner, PDI Security and Network Solutions, on their many efforts to consolidate information in the weekly report.